Gene Detail
Contact
Missing content? – Request curation!
Request curation for specific Genes, Variants, or PubMed publications.
Have questions, comments, or suggestions? - Let us know!
Email us at : ckbsupport@jax.org
| Gene Symbol | PBRM1 | ||||||||||
| Synonyms | BAF180 | PB1 | RCC | SMARCH1 | ||||||||||
| Gene Description | PBRM1, polybromo 1, is a member of the PBAF subunit (PMID: 32303701) of the SWI/SNF complex, which functions in chromatin remodeling to modulate gene expression (PMID: 23867514). PBRM1 is frequently mutated in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (PMID: 19084573, PMID: 31861590). | ||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
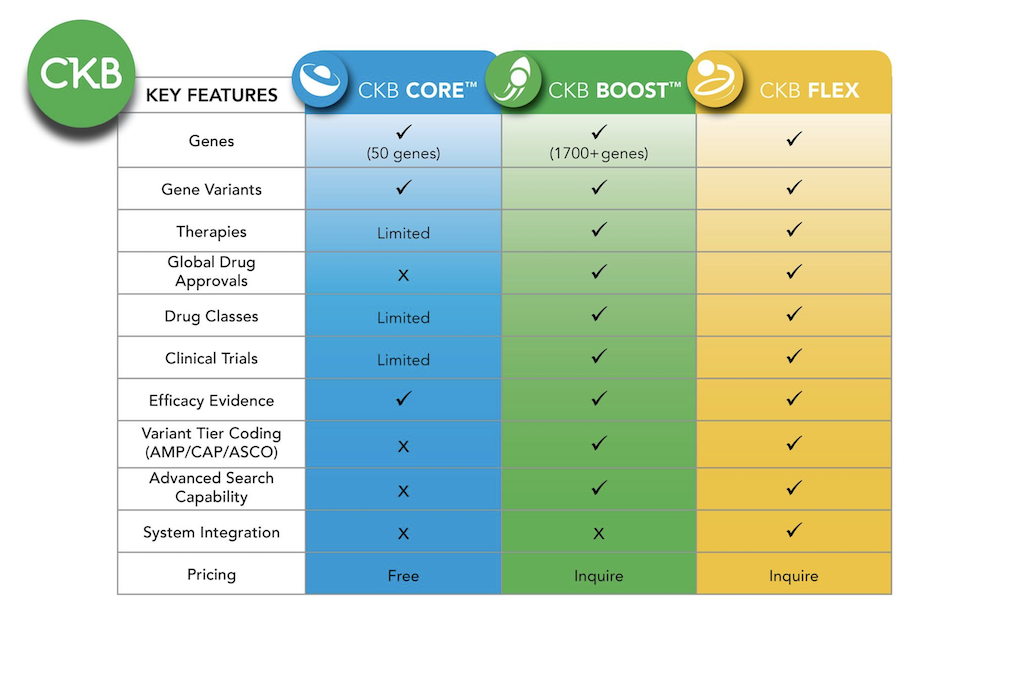
Additional content available in  CKB BOOST
CKB BOOST