Gene Detail
Contact
Missing content? – Request curation!
Request curation for specific Genes, Variants, or PubMed publications.
Have questions, comments, or suggestions? - Let us know!
Email us at : ckbsupport@jax.org
| Gene Symbol | MPL | ||||||||||
| Synonyms | C-MPL | CD110 | MPLV | THCYT2 | THPOR | TPOR | ||||||||||
| Gene Description | MPL, MPL proto-oncogene, thrombopoietin receptor, binds the cytokine, thrombopoietin, to induce signaling of JAK2 and TYK2 to activate several signal transduction pathways to control blood cell development (PMID: 16834459, PMID: 28408900). MPL mutations are often found in myeloproliferative neoplasms (PMID: 27727468, PMID: 31858134, PMID: 31750750). | ||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
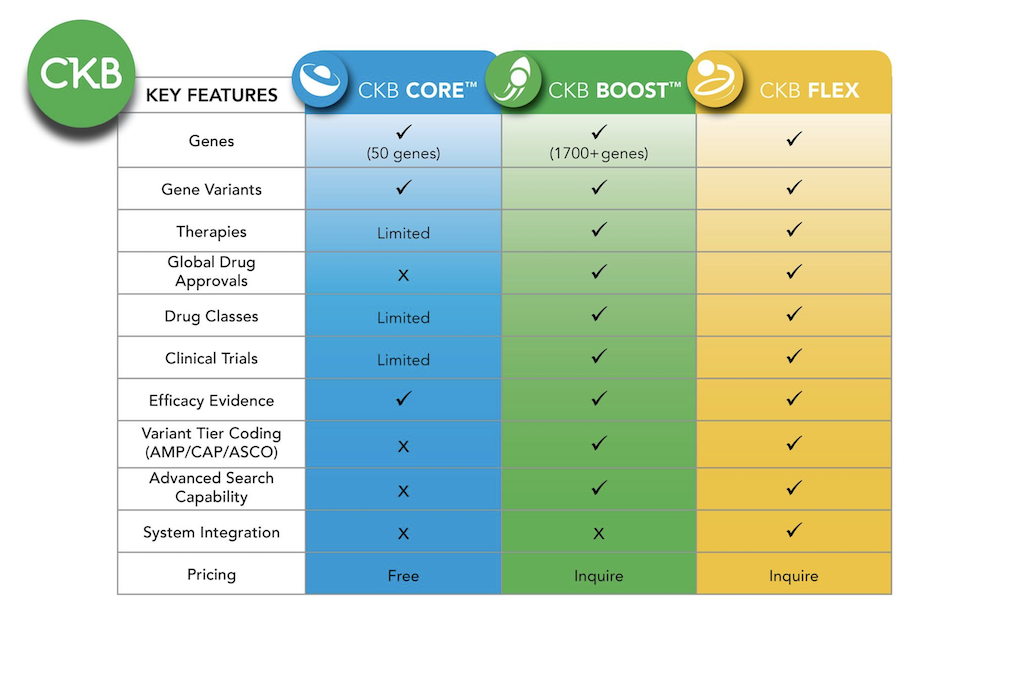
Additional content available in  CKB BOOST
CKB BOOST