Gene Detail
Contact
Missing content? – Request curation!
Request curation for specific Genes, Variants, or PubMed publications.
Have questions, comments, or suggestions? - Let us know!
Email us at : ckbsupport@jax.org
| Gene Symbol | POLE | ||||||||||
| Synonyms | CRCS12 | FILS | IMAGEI | POLE1 | ||||||||||
| Gene Description | POLE, DNA polymerase epsilon catalytic subunit, mediates proofreading activity during DNA repair and replication (PMID: 26822575, PMID: 29604063) and plays a role in genomic stability (PMID: 31747945). Somatic mutations in POLE have been identified in colorectal cancer (PMID: 29998005, PMID: 29072370), frequently in endometrial cancer (PMID: 26822575, PMID: 28795426, PMID: 30733993), and are often associated with high tumor mutational burden (PMID: 30733993, PMID: 29880869), but are less likely to be associated with DNA mismatch repair (MMR) deficiency (PMID: 30585826). | ||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
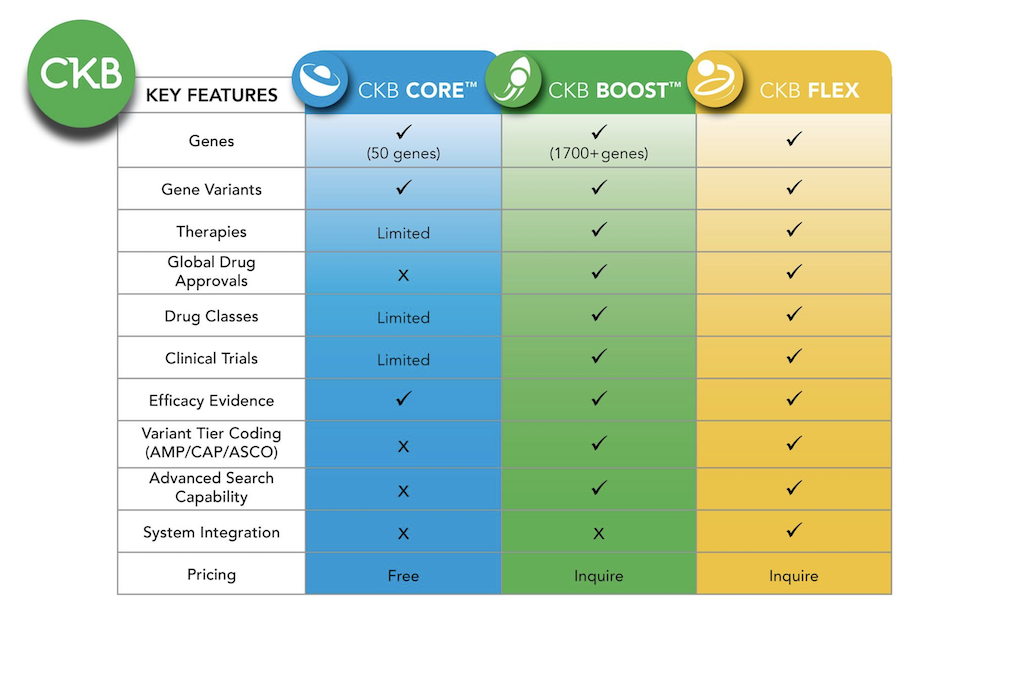
Additional content available in  CKB BOOST
CKB BOOST